我们最近发布了 Claude Code,这是一个用于智能编程的命令行工具。作为研究项目开发,Claude Code 为 Anthropic 的工程师和研究人员提供了一种更原生的方式,将 Claude 集成到他们的编程工作流程中。
Claude Code 有意设计为低级且无偏见的工具,提供接近原始模型访问的能力,而不强制特定的工作流程。这种设计理念创造了一个灵活、可定制、可脚本化且安全的强大工具。虽然功能强大,但这种灵活性为初次接触智能编程工具的工程师带来了学习曲线——至少在他们形成自己的最佳实践之前是如此。
本文概述了经过验证有效的一般模式,这些模式既适用于 Anthropic 的内部团队,也适用于在各种代码库、语言和环境中使用 Claude Code 的外部工程师。此列表中的内容并非一成不变,也不具有普遍适用性;请将这些建议视为起点。我们鼓励你进行实验,找到最适合你的方法!
需要更详细的信息?我们在 claude.ai/code 的全面文档涵盖了本文提到的所有功能,并提供了额外的示例、实现细节和高级技术。
1. 自定义你的设置
Claude Code 是一个代理编码助手,会自动将上下文信息拉入提示中。这种上下文收集会消耗时间和令牌,但你可以通过环境调优来优化它。
a. 创建 CLAUDE.md 文件
CLAUDE.md 是一个特殊文件,Claude 在开始对话时会自动将其拉入上下文中。这使其成为记录以下内容的理想位置:
- 常用 bash 命令
- 核心文件和实用函数
- Code style guidelines 代码风格指南
- Testing instructions 测试说明
- 代码仓库规范(例如分支命名、合并与变基等)
- 开发环境设置(例如,pyenv 使用、哪些编译器可用)
- 项目特有的任何异常行为或警告
- 您希望 Claude 记住的其他信息
CLAUDE.md 文件没有必需的格式。我们建议保持简洁和易读。例如:
# Bash commands
- npm run build: Build the project
- npm run typecheck: Run the typechecker
# Code style
- Use ES modules (import/export) syntax, not CommonJS (require)
- Destructure imports when possible (eg. import { foo } from 'bar')
# Workflow
- Be sure to typecheck when you’re done making a series of code changes
- Prefer running single tests, and not the whole test suite, for performance
您可以将 CLAUDE.md 文件放置在以下几个位置:
- The root of your repo, or wherever you run
claudefrom (the most common usage). Name itCLAUDE.mdand check it into git so that you can share it across sessions and with your team (recommended), or name itCLAUDE.local.mdand.gitignoreit
仓库的根目录,或者您运行claude的任何位置(最常见的用法)。将其命名为CLAUDE.md并检入 git,这样您就可以在会话之间和团队中共享它(推荐),或者将其命名为CLAUDE.local.md并.gitignore它 - Any parent of the directory where you run
claude. This is most useful for monorepos, where you might runclaudefromroot/foo, and haveCLAUDE.mdfiles in bothroot/CLAUDE.mdandroot/foo/CLAUDE.md. Both of these will be pulled into context automatically
您运行claude的目录的任何父目录。这对单一仓库最有用,您可能从root/foo运行claude,并在root/CLAUDE.md和root/foo/CLAUDE.md中都有CLAUDE.md文件。这两个文件都会自动拉入上下文中 - Any child of the directory where you run
claude. This is the inverse of the above, and in this case, Claude will pull inCLAUDE.mdfiles on demand when you work with files in child directories
您运行claude的目录的任何子目录。这与上述情况相反,在这种情况下,当您处理子目录中的文件时,Claude 会按需拉入CLAUDE.md文件 - Your home folder (
~/.claude/CLAUDE.md), which applies it to all your claude sessions
您的主文件夹(~/.claude/CLAUDE.md),它适用于您的所有 Claude 会话
当您运行 /init 命令时,Claude 会自动为您生成一个 CLAUDE.md 。
b. 调整您的 CLAUDE.md 文件
您的 CLAUDE.md 文件会成为 Claude 提示的一部分,因此应该像任何经常使用的提示一样进行优化。一个常见的错误是添加大量内容而不迭代其有效性。花时间进行实验,确定什么能让模型产生最佳的指令遵循效果。
您可以手动向 CLAUDE.md 添加内容,或按 # 键给 Claude 一个指令,它会自动将其纳入相关的 CLAUDE.md 中。许多工程师在编码时经常使用 # 来记录命令、文件和样式指南,然后在提交中包含 CLAUDE.md 更改,这样团队成员也能受益。
At Anthropic, we occasionally run CLAUDE.md files through the prompt improver and often tune instructions (e.g. adding emphasis with “IMPORTANT” or “YOU MUST”) to improve adherence.
在 Anthropic,我们偶尔会通过提示改进器运行 CLAUDE.md 文件,并经常调整指令(例如,添加”重要”或”您必须”等强调内容)以提高遵从性。
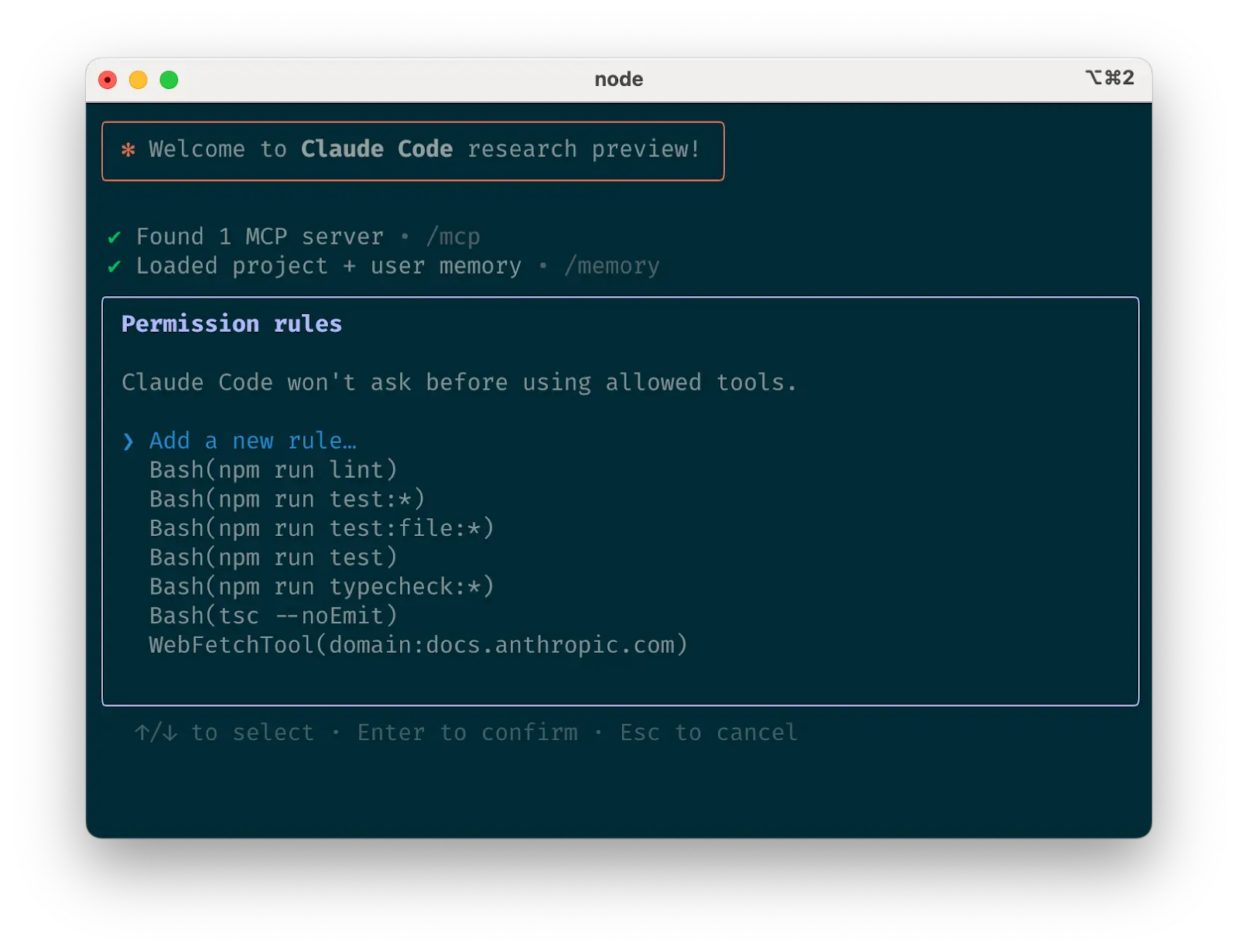
Claude Code tool allowlist
c. Curate Claude’s list of allowed toolsc. 管理 Claude 的允许工具列表
默认情况下,Claude Code 会对任何可能修改您系统的操作请求权限:文件写入、许多 bash 命令、MCP 工具等。我们在设计 Claude Code 时故意采用这种保守的方法来优先保障安全性。您可以自定义允许列表,以允许您知道安全的其他工具,或允许容易撤销的潜在不安全工具(例如,文件编辑、 git commit )。
There are four ways to manage allowed tools:
有四种方式来管理允许的工具:
- Select “Always allow” when prompted during a session.
在会话期间出现提示时选择”始终允许”。 - Use the
/permissionscommand after starting Claude Code to add or remove tools from the allowlist. For example, you can addEditto always allow file edits,Bash(git commit:*)to allow git commits, ormcp__puppeteer__puppeteer_navigateto allow navigating with the Puppeteer MCP server.
启动 Claude Code 后使用/permissions命令从允许列表中添加或移除工具。例如,您可以添加Edit来始终允许文件编辑,添加Bash(git commit:*)来允许 git 提交,或添加mcp__puppeteer__puppeteer_navigate来允许使用 Puppeteer MCP 服务器进行导航。 - Manually edit your
.claude/settings.jsonor~/.claude.json(we recommend checking the former into source control to share with your team).
手动编辑您的.claude/settings.json或~/.claude.json(我们建议将前者检入源代码控制以便与团队共享)。 - Use the
--allowedToolsCLI flag for session-specific permissions.
使用--allowedToolsCLI 标志进行会话特定权限设置。
d. If using GitHub, install the gh CLId. 如果使用 GitHub,请安装 gh CLI
Claude knows how to use the gh CLI to interact with GitHub for creating issues, opening pull requests, reading comments, and more. Without gh installed, Claude can still use the GitHub API or MCP server (if you have it installed).
Claude 知道如何使用 gh CLI 与 GitHub 交互,用于创建议题、开启拉取请求、阅读评论等操作。如果没有安装 gh ,Claude 仍然可以使用 GitHub API 或 MCP 服务器(如果您已安装)。
Claude has access to your shell environment, where you can build up sets of convenience scripts and functions for it just like you would for yourself. It can also leverage more complex tools through MCP and REST APIs.
Claude 可以访问你的 Shell 环境,你可以像为自己构建一样,为它构建一套便利脚本和函数。它还可以通过 MCP 和 REST API 利用更复杂的工具。
a. Use Claude with bash toolsa. 使用带有 bash 工具的 Claude
Claude Code inherits your bash environment, giving it access to all your tools. While Claude knows common utilities like unix tools and gh, it won’t know about your custom bash tools without instructions:
Claude 代码继承了你的 bash 环境,使其能够访问你所有的工具。虽然 Claude 了解常见的实用程序,如 unix 工具和 gh ,但如果没有说明,它不会了解你的自定义 bash 工具:
- Tell Claude the tool name with usage examples
告诉 Claude 工具名称并提供使用示例 - Tell Claude to run
--helpto see tool documentation
告诉 Claude 运行--help来查看工具文档 - Document frequently used tools in
CLAUDE.md
在CLAUDE.md中记录常用工具
b. Use Claude with MCPb. 将 Claude 与 MCP 结合使用
Claude Code functions as both an MCP server and client. As a client, it can connect to any number of MCP servers to access their tools in three ways:
Claude Code 既可以作为 MCP 服务器也可以作为客户端运行。作为客户端,它可以连接到任意数量的 MCP 服务器,通过三种方式访问它们的工具:
- In project config (available when running Claude Code in that directory)
在项目配置中(在该目录中运行 Claude Code 时可用) - In global config (available in all projects)
在全局配置中(在所有项目中都可用) - In a checked-in
.mcp.jsonfile (available to anyone working in your codebase). For example, you can add Puppeteer and Sentry servers to your.mcp.json, so that every engineer working on your repo can use these out of the box.
在签入的.mcp.json文件中(对在你的代码库中工作的任何人都可用)。例如,你可以将 Puppeteer 和 Sentry 服务器添加到你的.mcp.json中,这样在你的代码库上工作的每个工程师都可以开箱即用这些功能。
When working with MCP, it can also be helpful to launch Claude with the --mcp-debug flag to help identify configuration issues.
在使用 MCP 时,使用 --mcp-debug 标志启动 Claude 也很有帮助,这有助于识别配置问题。
c. Use custom slash commandsc. 使用自定义斜杠命令
For repeated workflows—debugging loops, log analysis, etc.—store prompt templates in Markdown files within the .claude/commands folder. These become available through the slash commands menu when you type /. You can check these commands into git to make them available for the rest of your team.
对于重复的工作流程——调试循环、日志分析等——将提示模板存储在 .claude/commands 文件夹内的 Markdown 文件中。当你输入 / 时,这些模板会通过斜杠命令菜单变得可用。你可以将这些命令签入 git,以便团队其他成员也能使用。
Custom slash commands can include the special keyword $ARGUMENTS to pass parameters from command invocation.
自定义斜杠命令可以包含特殊关键字 $ARGUMENTS 来传递命令调用中的参数。
For example, here’s a slash command that you could use to automatically pull and fix a Github issue:
例如,这里有一个斜杠命令,你可以用它来自动拉取和修复 Github 问题:
Putting the above content into .claude/commands/fix-github-issue.md makes it available as the /project:fix-github-issue command in Claude Code. You could then for example use /project:fix-github-issue 1234 to have Claude fix issue #1234. Similarly, you can add your own personal commands to the ~/.claude/commands folder for commands you want available in all of your sessions.
3. Try common workflows 3. 尝试常见工作流程
Claude Code doesn’t impose a specific workflow, giving you the flexibility to use it how you want. Within the space this flexibility affords, several successful patterns for effectively using Claude Code have emerged across our community of users:
Claude Code 不会强制要求特定的工作流程,让您可以灵活地按照自己想要的方式使用它。在这种灵活性所提供的空间内,我们的用户社区中已经涌现出了几种成功有效使用 Claude Code 的模式:
a. 探索、规划、编码、提交
这种多功能的工作流程适用于许多问题:
- 要求 Claude 读取相关文件、图像或 URL,提供一般性指导(“读取处理日志记录的文件”)或具体文件名(“读取 logging.py”),但明确告诉它暂时不要编写任何代码。
- 这是工作流程中应考虑大量使用子代理的部分,特别是对于复杂问题。告诉 Claude 使用子代理来验证细节或调查它可能遇到的特定问题,尤其是在对话或任务的早期阶段,往往能够保持上下文可用性,而在效率损失方面没有太大的负面影响。
- 要求 Claude 制定解决特定问题的计划。我们建议使用”think”这个词来触发扩展思考模式,这能给 Claude 额外的计算时间来更全面地评估各种选择。这些特定短语直接对应系统中递增的思考预算级别:"think" < "think hard" < "think harder" < "ultrathink"。每个级别都为 Claude 分配渐进式增加的思考预算。
- If the results of this step seem reasonable, you can have Claude create a document or a GitHub issue with its plan so that you can reset to this spot if the implementation (step 3) isn’t what you want.
如果这一步的结果看起来合理,你可以让 Claude 创建一个文档或 GitHub issue 来记录它的计划,这样如果实现过程(第 3 步)不符合你的预期,你可以回到这个节点。
- If the results of this step seem reasonable, you can have Claude create a document or a GitHub issue with its plan so that you can reset to this spot if the implementation (step 3) isn’t what you want.
- 要求 Claude 用代码实现它的解决方案。这也是一个很好的时机,可以要求它在实现解决方案的各个部分时明确验证其解决方案的合理性。
- 要求 Claude 提交结果并创建拉取请求。如果相关的话,这也是让 Claude 更新任何 README 文件或更改日志的好时机,说明它刚才做了什么。
第 1-2 步至关重要——没有这些步骤,Claude 往往会直接跳到编码解决方案。虽然有时这正是你想要的,但让 Claude 先进行研究和规划能显著提高需要深度前期思考的问题的性能表现。
b. Write tests, commit; code, iterate, commitb. 编写测试,提交;编写代码,迭代,提交
This is an Anthropic-favorite workflow for changes that are easily verifiable with unit, integration, or end-to-end tests. Test-driven development (TDD) becomes even more powerful with agentic coding:
这是 Anthropic 最喜欢的工作流程,适用于可以通过单元测试、集成测试或端到端测试轻松验证的更改。测试驱动开发(TDD)在智能体编码中变得更加强大:
- Ask Claude to write tests based on expected input/output pairs. Be explicit about the fact that you’re doing test-driven development so that it avoids creating mock implementations, even for functionality that doesn’t exist yet in the codebase.
要求 Claude 基于预期的输入/输出对编写测试。明确告诉它你正在进行测试驱动开发,这样它就会避免创建模拟实现,即使对于代码库中尚不存在的功能也是如此。 - Tell Claude to run the tests and confirm they fail. Explicitly telling it not to write any implementation code at this stage is often helpful.
告诉 Claude 运行测试并确认它们失败。在这个阶段明确告诉它不要编写任何实现代码通常是有帮助的。 - Ask Claude to commit the tests when you’re satisfied with them.
当你对测试满意时,要求 Claude 提交这些测试。 - Ask Claude to write code that passes the tests, instructing it not to modify the tests. Tell Claude to keep going until all tests pass. It will usually take a few iterations for Claude to write code, run the tests, adjust the code, and run the tests again.
要求 Claude 编写通过测试的代码,并指示它不要修改测试。告诉 Claude 继续工作直到所有测试都通过。通常需要几次迭代,Claude 会编写代码、运行测试、调整代码,然后再次运行测试。- At this stage, it can help to ask it to verify with independent subagents that the implementation isn’t overfitting to the tests
在这个阶段,可以要求它通过独立的子代理来验证实现没有过度拟合测试
- At this stage, it can help to ask it to verify with independent subagents that the implementation isn’t overfitting to the tests
- Ask Claude to commit the code once you’re satisfied with the changes.
当你对更改满意后,要求 Claude 提交代码。
Claude performs best when it has a clear target to iterate against—a visual mock, a test case, or another kind of output. By providing expected outputs like tests, Claude can make changes, evaluate results, and incrementally improve until it succeeds.
当 Claude 有明确的迭代目标时表现最佳——视觉模型、测试用例或其他类型的输出。通过提供预期输出如测试,Claude 可以进行更改、评估结果,并逐步改进直到成功。
c. Write code, screenshot result, iteratec. 编写代码,截图结果,迭代优化
Similar to the testing workflow, you can provide Claude with visual targets:
与测试工作流程类似,你可以为 Claude 提供视觉目标:
- Give Claude a way to take browser screenshots (e.g., with the Puppeteer MCP server, an iOS simulator MCP server, or manually copy / paste screenshots into Claude).
为 Claude 提供浏览器截图功能(例如,使用 Puppeteer MCP 服务器、iOS 模拟器 MCP 服务器,或手动复制/粘贴截图到 Claude 中)。 - Give Claude a visual mock by copying / pasting or drag-dropping an image, or giving Claude the image file path.
通过复制/粘贴或拖放图片的方式为 Claude 提供视觉模拟图,或直接给 Claude 提供图片文件路径。 - Ask Claude to implement the design in code, take screenshots of the result, and iterate until its result matches the mock.
让 Claude 实现设计代码,截取结果截图,并反复迭代直到结果与模型匹配。 - Ask Claude to commit when you’re satisfied.
当您满意时,让 Claude 提交代码。
Like humans, Claude’s outputs tend to improve significantly with iteration. While the first version might be good, after 2-3 iterations it will typically look much better. Give Claude the tools to see its outputs for best results.
与人类一样,Claude 的输出结果往往通过迭代显著改善。虽然第一版可能不错,但经过 2-3 次迭代后,通常会看起来好得多。为了获得最佳结果,请为 Claude 提供查看其输出结果的工具。
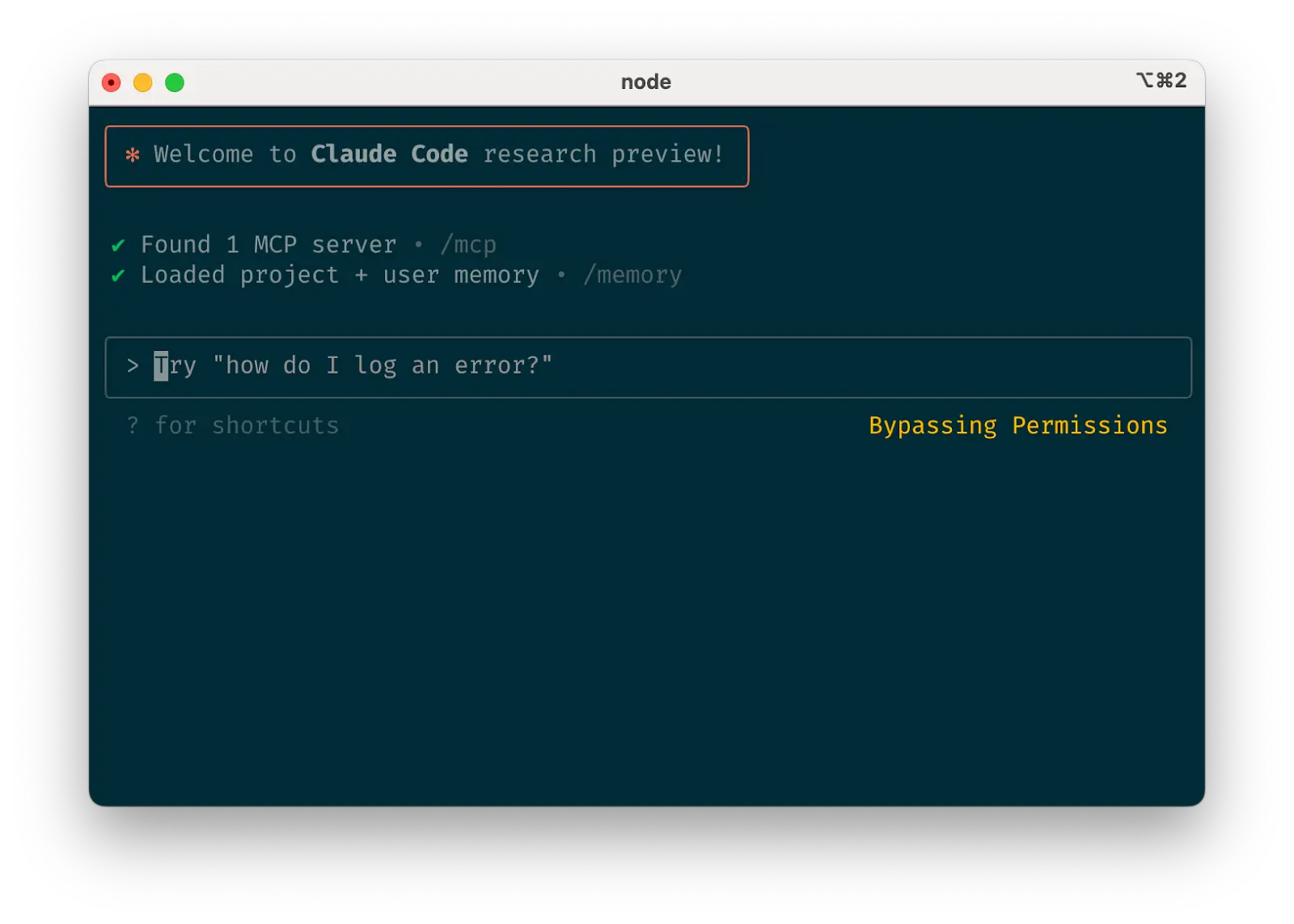
Safe yolo mode
d. Safe YOLO mode d. 安全 YOLO 模式
你可以使用 claude --dangerously-skip-permissions 来绕过所有权限检查,让 Claude 不受干扰地工作直到完成,而不是监督 Claude。这对于修复 lint 错误或生成样板代码等工作流程很有效。
让 Claude 运行任意命令是有风险的,可能导致数据丢失、系统损坏,甚至数据泄露(例如,通过提示注入攻击)。为了最小化这些风险,请在没有互联网访问的容器中使用 --dangerously-skip-permissions 。你可以参考使用 Docker Dev Containers 的参考实现。
e. Codebase Q&A e. 代码库问答
在接触新代码库时,可以使用 Claude Code 进行学习和探索。你可以向 Claude 提出与结对编程时向其他工程师提出的相同类型的问题。Claude 可以主动搜索代码库来回答一般性问题,比如:
- How does logging work?日志记录是如何工作的?
- How do I make a new API endpoint?
如何创建新的 API 端点? - What does
async move { ... }do on line 134 offoo.rs?
foo.rs文件第 134 行的async move { ... }是做什么的? - What edge cases does
CustomerOnboardingFlowImplhandle?
CustomerOnboardingFlowImpl处理哪些边缘情况? - Why are we calling
foo()instead ofbar()on line 333?
为什么我们在第 333 行调用foo()而不是bar()? - What’s the equivalent of line 334 of
baz.pyin Java?
baz.py第 334 行在 Java 中的等价代码是什么?
在 Anthropic,以这种方式使用 Claude Code 已经成为我们核心的入职培训流程,显著改善了上手时间并减少了其他工程师的负担。无需特殊提示!只需提出问题,Claude 就会探索代码来找到答案。
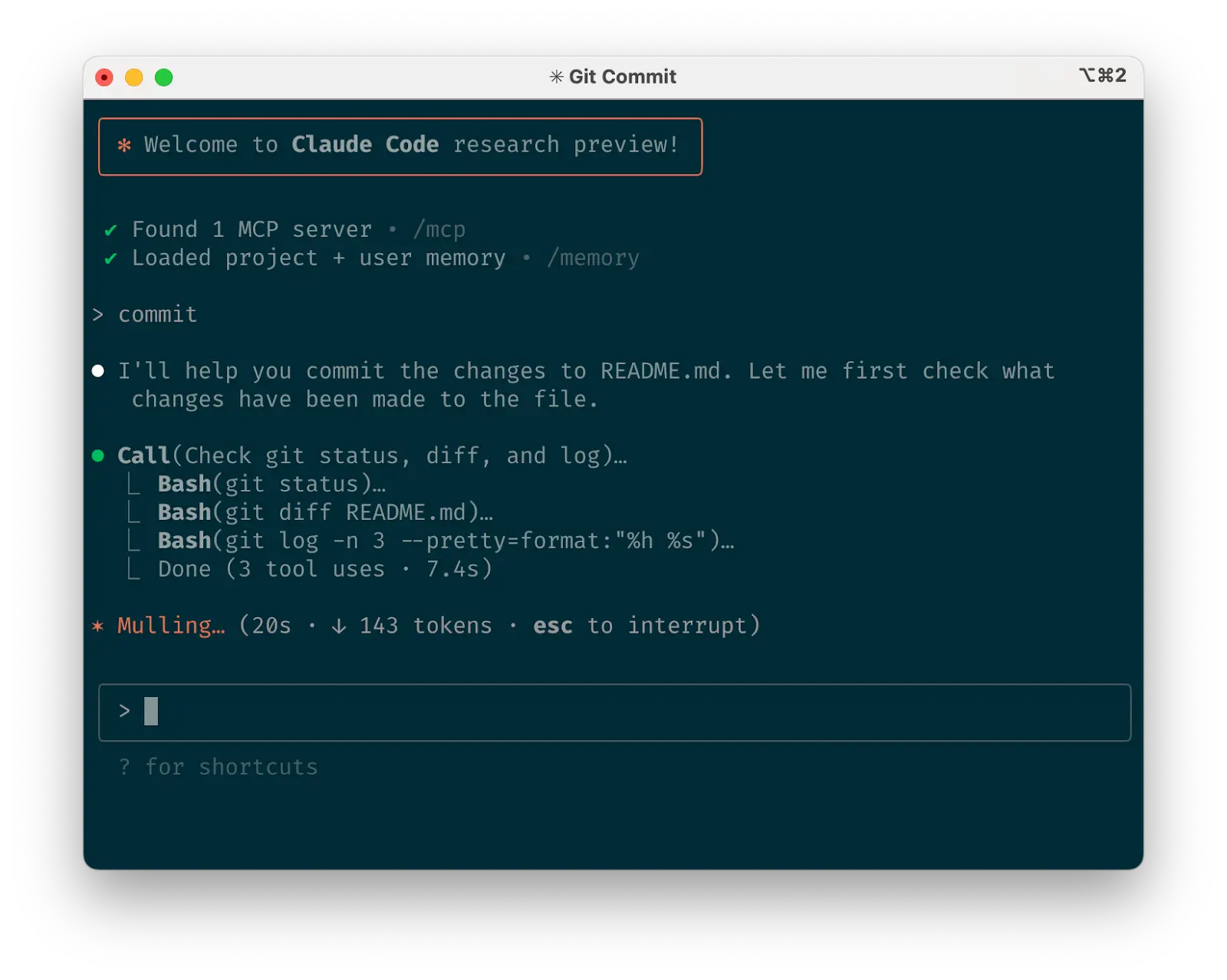
Use Claude to interact with git
f. Use Claude to interact with gitf. 使用 Claude 与 git 交互
Claude can effectively handle many git operations. Many Anthropic engineers use Claude for 90%+ of our git interactions:
Claude 可以有效处理许多 git 操作。许多 Anthropic 工程师在 90% 以上的 git 交互中都使用 Claude:
- Searching git history to answer questions like “What changes made it into v1.2.3?”, “Who owns this particular feature?”, or “Why was this API designed this way?” It helps to explicitly prompt Claude to look through git history to answer queries like these.
搜索 git 历史来回答诸如”v1.2.3 版本包含了哪些更改?”、“谁负责这个特定功能?“或”为什么 API 要这样设计?“等问题。明确提示 Claude 查看 git 历史来回答此类查询会很有帮助。 - Writing commit messages.Claude will look at your changes and recent history automatically to compose a message taking all the relevant context into account
编写提交信息。Claude 会自动查看你的更改和最近的历史记录,综合所有相关上下文来撰写信息 - Handling complex git operations like reverting files, resolving rebase conflicts, and comparing and grafting patches
处理复杂的 git 操作,如恢复文件、解决变基冲突,以及比较和移植补丁
g. Use Claude to interact with GitHubg. 使用 Claude 与 GitHub 交互
Claude Code can manage many GitHub interactions:
Claude Code 可以管理许多 GitHub 交互:
- Creating pull requests: Claude understands the shorthand “pr” and will generate appropriate commit messages based on the diff and surrounding context.
创建拉取请求:Claude 理解简写”pr”,并将根据差异和周围上下文生成适当的提交消息。 - Implementing one-shot resolutions for simple code review comments: just tell it to fix comments on your PR (optionally, give it more specific instructions) and push back to the PR branch when it’s done.
为简单的代码审查评论实现一次性解决方案:只需告诉它修复你 PR 上的评论(可选择性地给出更具体的指示),完成后推送回 PR 分支。 - Fixing failing builds or linter warnings
修复构建失败或代码检查警告 - Categorizing and triaging open issues by asking Claude to loop over open GitHub issues
通过让 Claude 遍历开放的 GitHub 问题来对开放问题进行分类和分流
This eliminates the need to remember gh command line syntax while automating routine tasks.
这消除了记忆 gh 命令行语法的需要,同时自动化了日常任务。
h. Use Claude to work with Jupyter notebooksh. 使用 Claude 处理 Jupyter 笔记本
Researchers and data scientists at Anthropic use Claude Code to read and write Jupyter notebooks. Claude can interpret outputs, including images, providing a fast way to explore and interact with data. There are no required prompts or workflows, but a workflow we recommend is to have Claude Code and a .ipynb file open side-by-side in VS Code.
Anthropic 的研究人员和数据科学家使用 Claude Code 来读写 Jupyter 笔记本。Claude 能够解释输出结果,包括图像,为探索和交互数据提供了一种快速的方法。虽然没有必需的提示或工作流程,但我们推荐的工作流程是在 VS Code 中并排打开 Claude Code 和一个 .ipynb 文件。
You can also ask Claude to clean up or make aesthetic improvements to your Jupyter notebook before you show it to colleagues. Specifically telling it to make the notebook or its data visualizations “aesthetically pleasing” tends to help remind it that it’s optimizing for a human viewing experience.
你还可以要求 Claude 在向同事展示之前清理或美化你的 Jupyter 笔记本。具体告诉它让笔记本或其数据可视化”在美观上令人愉悦”,往往有助于提醒它正在为人类观看体验进行优化。
4. 优化你的工作流程
以下建议适用于所有工作流程:
a. 在指令中要具体明确
Claude 代码生成的成功率在更具体的指令下会显著提高,尤其是在首次尝试时。预先给出清晰的方向可以减少后续修正的需要。
For example:例如:
| Poor 不好的示例 | Good 好 |
|---|---|
| add tests for foo.py 为 foo.py 添加测试 | write a new test case for foo.py, covering the edge case where the user is logged out. avoid mocks 为 foo.py 编写一个新的测试用例,覆盖用户已退出登录的边界情况。避免使用模拟对象 |
| why does ExecutionFactory have such a weird api? 为什么 ExecutionFactory 有如此奇怪的 API? | look through ExecutionFactory’s git history and summarize how its api came to be 查看 ExecutionFactory 的 git 历史记录并总结其 API 的形成过程 |
| add a calendar widget 添加日历小部件 | look at how existing widgets are implemented on the home page to understand the patterns and specifically how code and interfaces are separated out. HotDogWidget.php is a good example to start with. then, follow the pattern to implement a new calendar widget that lets the user select a month and paginate forwards/backwards to pick a year. Build from scratch without libraries other than the ones already used in the rest of the codebase. 查看主页上现有小部件的实现方式,了解相关模式,特别是代码和接口是如何分离的。HotDogWidget.php 是一个很好的入门示例。然后,按照该模式实现一个新的日历小部件,让用户能够选择月份并可以前后翻页来选择年份。除了代码库中已经使用的库之外,不使用其他库从头开始构建。 |
Claude 可以推断意图,但它无法读心。具体性能让结果更好地符合期望。
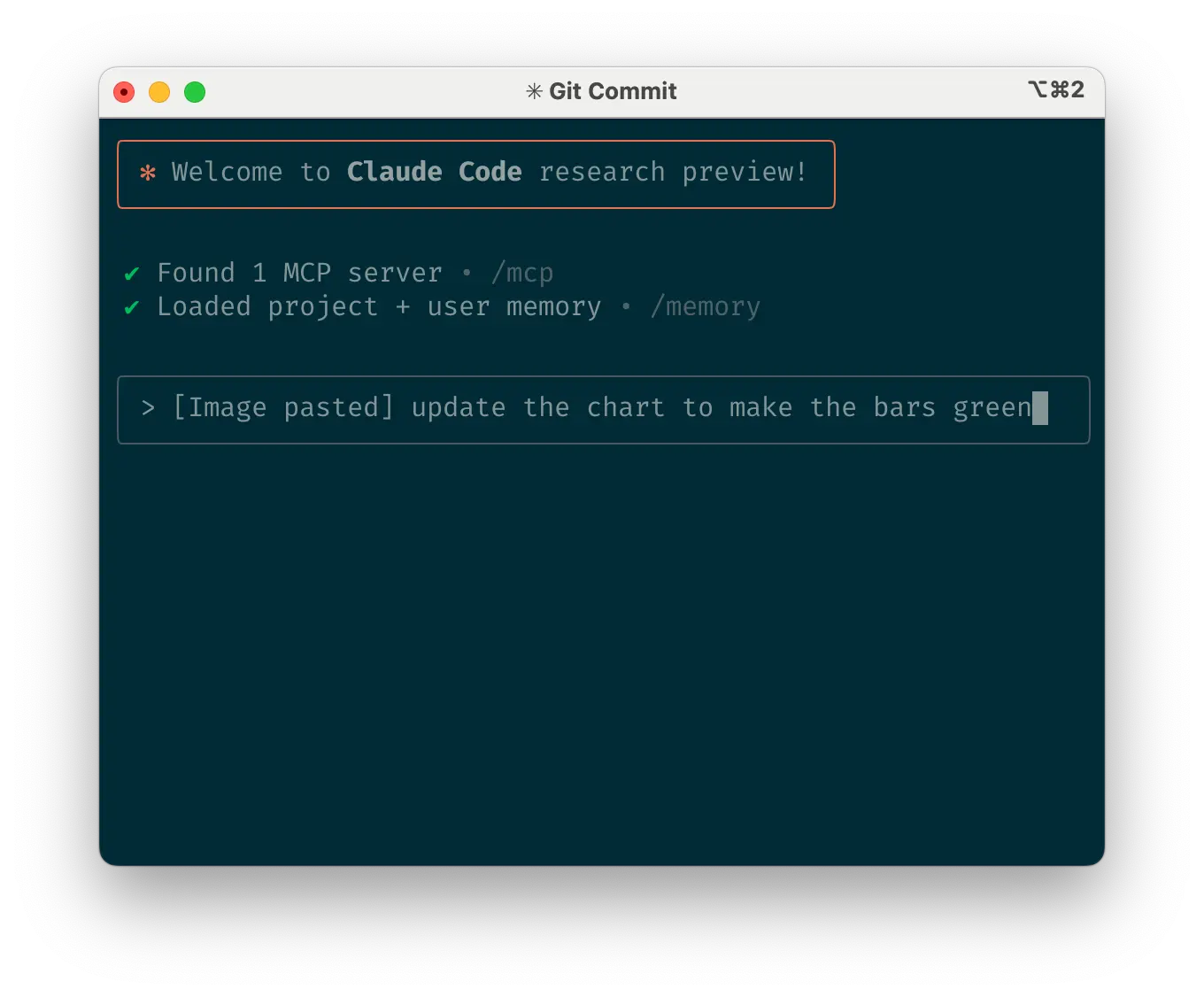
Give Claude images
b. 向 Claude 提供图像
Claude 在处理图像和图表方面表现出色,可以通过多种方式:
- Paste screenshots (pro tip: hit cmd+ctrl+shift+4 in macOS to screenshot to clipboard and ctrl+v to paste. Note that this is not cmd+v like you would usually use to paste on mac and does not work remotely.)
粘贴截图(专业提示:在 macOS 中按 cmd+ctrl+shift+4 截图到剪贴板,然后按 ctrl+v 粘贴。注意这里是 ctrl+v 而不是通常在 Mac 上使用的 cmd+v,且不支持远程操作。) - Drag and drop images directly into the prompt input
直接拖拽图像到提示输入框中 - Provide file paths for images
提供图像的文件路径
这在将设计稿作为 UI 开发参考点以及将可视化图表用于分析和调试时特别有用。如果您没有将视觉元素添加到上下文中,明确告诉 Claude 结果在视觉吸引力方面的重要性仍然会有所帮助。
Mention files you want Claude to look at or work on
c. 提及你希望 Claude 查看或处理的文件
使用制表符补全功能可以快速引用代码仓库中任何位置的文件或文件夹,帮助 Claude 找到或更新正确的资源。
Give Claude URLs
d. 为 Claude 提供 URL
在你的提示词旁边粘贴具体的 URL,让 Claude 获取并阅读内容。为了避免对相同域名(如 docs.foo.com)重复出现权限提示,使用 /permissions 将域名添加到你的允许列表中。
e. 及早并经常进行纠偏
虽然自动接受模式(shift+tab 切换)让 Claude 能够自主工作,但通过积极协作和引导 Claude 的方法,你通常会获得更好的结果。通过在开始时向 Claude 详细解释任务,你可以获得最佳结果,但你也可以随时对 Claude 进行纠偏。
These four tools help with course correction:
这四个工具有助于纠偏:
- Ask Claude to make a plan before coding. Explicitly tell it not to code until you’ve confirmed its plan looks good.
让 Claude 在编码前制定计划。明确告诉它在你确认计划看起来不错之前不要编码。 - Press Escape to interrupt Claude during any phase (thinking, tool calls, file edits), preserving context so you can redirect or expand instructions.
按 Escape 键可在任何阶段(思考、工具调用、文件编辑)中断 Claude,同时保留上下文,这样你就可以重新引导或扩展指令。 - Double-tap Escape to jump back in history, edit a previous prompt, and explore a different direction. You can edit the prompt and repeat until you get the result you’re looking for.
双击 Escape 键可回到历史记录,编辑之前的提示,并探索不同的方向。你可以编辑提示并重复操作,直到获得你想要的结果。 - Ask Claude to undo changes, often in conjunction with option #2 to take a different approach.
要求 Claude 撤销更改,通常与第 2 个选项结合使用,以采取不同的方法。
虽然 Claude Code 偶尔能在第一次尝试时完美解决问题,但使用这些纠错工具通常能更快地产生更好的解决方案。
f. 使用 /clear 保持上下文聚焦
在长时间的会话中,Claude 的上下文窗口可能会被无关的对话、文件内容和命令填满。这可能会降低性能,有时还会分散 Claude 的注意力。在任务之间频繁使用 /clear 命令来重置上下文窗口。
g. 对复杂工作流程使用清单和草稿本
对于具有多个步骤或需要详尽解决方案的大型任务——例如代码迁移、修复大量代码检查错误或运行复杂的构建脚本——可以通过让 Claude 使用 Markdown 文件(甚至是 GitHub issue!)作为检查清单和工作草稿来提高性能:
例如,要修复大量代码检查问题,您可以执行以下操作:
- Tell Claude to run the lint command and write all resulting errors (with filenames and line numbers) to a Markdown checklist
让 Claude 运行代码检查命令,并将所有产生的错误(包含文件名和行号)写入 Markdown 检查清单 - Instruct Claude to address each issue one by one, fixing and verifying before checking it off and moving to the next
指示 Claude 逐一处理每个问题,在修复和验证后勾选该问题,然后继续处理下一个
h. 向 Claude 传递数据
Several methods exist for providing data to Claude:
有几种方法可以向 Claude 提供数据:
- Copy and paste directly into your prompt (most common approach)
直接复制粘贴到提示中(最常见的方法) - Pipe into Claude Code (e.g.,
cat foo.txt | claude), particularly useful for logs, CSVs, and large data
通过管道输入到 Claude Code(例如,cat foo.txt | claude),对于日志、CSV 和大型数据特别有用 - Tell Claude to pull data via bash commands, MCP tools, or custom slash commands
告诉 Claude 通过 bash 命令、MCP 工具或自定义斜杠命令拉取数据 - Ask Claude to read files or fetch URLs (works for images too)
要求 Claude 读取文件或获取 URL(对图像也有效)
Most sessions involve a combination of these approaches. For example, you can pipe in a log file, then tell Claude to use a tool to pull in additional context to debug the logs.
大多数会话都涉及这些方法的组合。例如,你可以导入一个日志文件,然后告诉 Claude 使用工具拉取额外的上下文来调试日志。
5. 使用无头模式自动化你的基础设施
Claude Code includes headless mode for non-interactive contexts like CI, pre-commit hooks, build scripts, and automation. Use the -p flag with a prompt to enable headless mode, and --output-format stream-json for streaming JSON output.
Claude Code 包含用于非交互式环境的无头模式,如 CI、预提交钩子、构建脚本和自动化。使用 -p 标志加提示来启用无头模式,使用 --output-format stream-json 来获取流式 JSON 输出。
Note that headless mode does not persist between sessions. You have to trigger it each session.
注意无头模式不会在会话之间持续存在。你需要在每个会话中重新触发它。
a. 使用 Claude 进行问题分类
Headless mode can power automations triggered by GitHub events, such as when a new issue is created in your repository. For example, the public Claude Code repository uses Claude to inspect new issues as they come in and assign appropriate labels.
无头模式可以驱动由 GitHub 事件触发的自动化,比如在你的代码仓库中创建新问题时。例如,公共 Claude Code 代码仓库使用 Claude 来检查新进来的问题并分配适当的标签。
b. 使用 Claude 作为代码检查工具
Claude Code can provide subjective code reviews beyond what traditional linting tools detect, identifying issues like typos, stale comments, misleading function or variable names, and more.
Claude Code 可以提供超越传统代码检查工具的主观代码审查,识别拼写错误、过时注释、误导性函数或变量名等问题。
6. 通过多 Claude 工作流程提升水平
Beyond standalone usage, some of the most powerful applications involve running multiple Claude instances in parallel:
除了独立使用外,一些最强大的应用程序涉及并行运行多个 Claude 实例:
a. 让一个 Claude 编写代码;使用另一个 Claude 进行验证
一个简单但有效的方法是让一个 Claude 编写代码,而另一个 Claude 来审查或测试它。类似于与多个工程师合作,有时拥有独立的上下文是有益的:
- Use Claude to write code
使用 Claude 编写代码 - Run
/clearor start a second Claude in another terminal
运行/clear或在另一个终端中启动第二个 Claude - Have the second Claude review the first Claude’s work
让第二个 Claude 审查第一个 Claude 的工作 - Start another Claude (or
/clearagain) to read both the code and review feedback
启动另一个 Claude(或再次/clear)来阅读代码和审查反馈 - Have this Claude edit the code based on the feedback
让这个 Claude 根据反馈编辑代码
你可以对测试做类似的事情:让一个 Claude 编写测试,然后让另一个 Claude 编写代码来使测试通过。你甚至可以让你的 Claude 实例彼此通信,方法是给它们分别的工作草稿板,并告诉它们写入哪一个和从哪一个读取。
这种分离通常比让单个 Claude 处理所有事情产生更好的结果。
b. 设置代码仓库的多个检出副本
Rather than waiting for Claude to complete each step, something many engineers at Anthropic do is:
许多 Anthropic 的工程师采用的做法是,而不是等待 Claude 完成每个步骤:
- Create 3-4 git checkouts in separate folders
在不同文件夹中创建 3-4 个 git 检出 - Open each folder in separate terminal tabs
在单独的终端标签页中打开每个文件夹 - Start Claude in each folder with different tasks
在每个文件夹中启动 Claude 并分配不同的任务 - Cycle through to check progress and approve/deny permission requests
循环检查进度并批准/拒绝权限请求
c. 使用 git 工作树
This approach shines for multiple independent tasks, offering a lighter-weight alternative to multiple checkouts. Git worktrees allow you to check out multiple branches from the same repository into separate directories. Each worktree has its own working directory with isolated files, while sharing the same Git history and reflog.
这种方法在处理多个独立任务时表现出色,为多重检出提供了一个更轻量级的替代方案。Git 工作树允许你从同一个代码仓库中将多个分支检出到不同的目录中。每个工作树都有自己独立的工作目录和隔离的文件,同时共享相同的 Git 历史记录和引用日志。
Using git worktrees enables you to run multiple Claude sessions simultaneously on different parts of your project, each focused on its own independent task. For instance, you might have one Claude refactoring your authentication system while another builds a completely unrelated data visualization component. Since the tasks don’t overlap, each Claude can work at full speed without waiting for the other’s changes or dealing with merge conflicts:
使用 git worktrees 可以让你在项目的不同部分同时运行多个 Claude 会话,每个会话专注于自己独立的任务。例如,你可能让一个 Claude 重构你的认证系统,同时另一个 Claude 构建一个完全不相关的数据可视化组件。由于任务不重叠,每个 Claude 都能全速工作,无需等待其他 Claude 的更改或处理合并冲突:
- Create worktrees:
git worktree add ../project-feature-a feature-a创建工作树:git worktree add ../project-feature-a feature-a - Launch Claude in each worktree:
cd ../project-feature-a && claude
在每个工作树中启动 Claude:cd ../project-feature-a && claude - Create additional worktrees as needed (repeat steps 1-2 in new terminal tabs)
根据需要创建额外的工作树(在新的终端标签页中重复步骤 1-2)
Some tips:一些提示:
- Use consistent naming conventions
使用一致的命名约定 - Maintain one terminal tab per worktree
为每个工作树保持一个终端标签页 - If you’re using iTerm2 on Mac, set up notifications for when Claude needs attention
如果你在 Mac 上使用 iTerm2,可以设置通知来提醒 Claude 需要关注的时候 - Use separate IDE windows for different worktrees
为不同的工作树使用单独的 IDE 窗口 - Clean up when finished:
git worktree remove ../project-feature-a
完成后清理:git worktree remove ../project-feature-a
d. 使用自定义工具使用无头模式
claude -p (headless mode) integrates Claude Code programmatically into larger workflows while leveraging its built-in tools and system prompt. There are two primary patterns for using headless mode:
claude -p (无头模式)将 Claude Code 以编程方式集成到更大的工作流程中,同时利用其内置工具和系统提示。使用无头模式有两种主要模式:
1. Fanning out handles large migrations or analyses (e.g., analyzing sentiment in hundreds of logs or analyzing thousands of CSVs):
1. 扇出处理大型迁移或分析(例如,分析数百条日志中的情感或分析数千个 CSV 文件):
- Have Claude write a script to generate a task list. For example, generate a list of 2k files that need to be migrated from framework A to framework B.
让 Claude 编写一个脚本来生成任务列表。例如,生成一个包含 2000 个需要从框架 A 迁移到框架 B 的文件列表。 - Loop through tasks, calling Claude programmatically for each and giving it a task and a set of tools it can use. For example:
claude -p “migrate foo.py from React to Vue. When you are done, you MUST return the string OK if you succeeded, or FAIL if the task failed.” --allowedTools Edit Bash(git commit:*)
循环遍历任务,为每个任务以编程方式调用 Claude,并为其提供任务和可使用的工具集。例如:claude -p “migrate foo.py from React to Vue. When you are done, you MUST return the string OK if you succeeded, or FAIL if the task failed.” --allowedTools Edit Bash(git commit:*) - Run the script several times and refine your prompt to get the desired outcome.
多次运行脚本并完善你的提示以获得期望的结果。
2. Pipelining integrates Claude into existing data/processing pipelines:
2. 流水线操作将 Claude 集成到现有的数据/处理流水线中:
- Call
claude -p “<your prompt>” --json | your_command, whereyour_commandis the next step of your processing pipeline
调用claude -p “<your prompt>” --json | your_command,其中your_command是处理流水线的下一步 - That’s it! JSON output (optional) can help provide structure for easier automated processing.
就是这样!JSON 输出(可选)可以帮助提供结构,以便更轻松地进行自动化处理。
对于这两种使用场景,使用 --verbose 标志来调试 Claude 调用会很有帮助。我们通常建议在生产环境中关闭详细模式,以获得更清洁的输出。
您在使用 Claude Code 时有什么技巧和最佳实践?请标记 @AnthropicAI,这样我们就能看到您正在构建的内容!